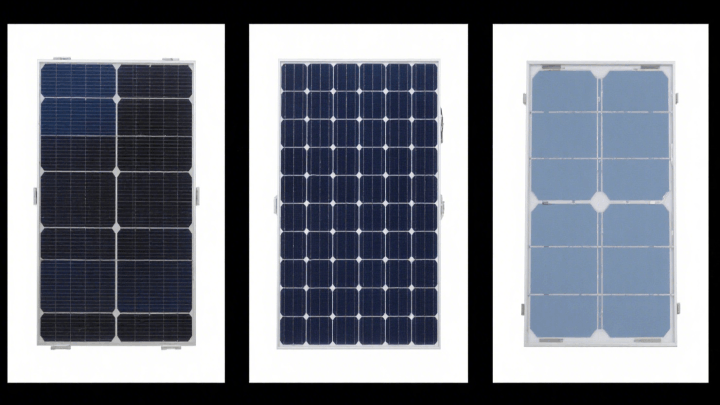
Photovoltaic glass
Photovoltaic glass (also known as PV glass)
is an important component of solar photovoltaic modules, mainly serving to protect the solar cells, transmit light, and support the components. Depending on its function, structure, and application scenario, it can be divided into the following main categories:
Classification by light transmittance and functionality
1. Ultra-clear rolled glass (mainstream type)
1.1 Features: Made from ultra-clear quartz sand and other raw materials, with extremely low iron content (typically <0.015%), achieving light transmittance of over 91% (in the 380-1100 nm wavelength range). This minimizes light absorption, thereby enhancing the photovoltaic conversion efficiency of solar panels.
1.2 Process: Produced using the rolled glass method, the surface typically features special textures (such as velvet or pyramid patterns) to reduce light reflection (reflectance as low as 8% or below) and enhance diffuse reflection, allowing more light to be absorbed by the solar cells.
1.3 Applications: Currently the most commonly used cover glass for photovoltaic modules, suitable for crystalline silicon photovoltaic modules (monocrystalline silicon, polycrystalline silicon).
2. Colored photovoltaic glass (special applications)
2.1 Features: Colored photovoltaic glass is produced by adding colorants (such as iron, cobalt, and other metal oxides) to achieve specific colors (e.g., blue, gray). Its light transmittance is slightly lower than that of ultra-clear glass (typically 80%-85%), but it offers aesthetic appeal and sunshade functionality.
2.2 Applications: Primarily used in the BIPV (Building-Integrated Photovoltaics) sector, such as photovoltaic facades and photovoltaic windows and doors, it balances power generation with architectural decoration requirements.
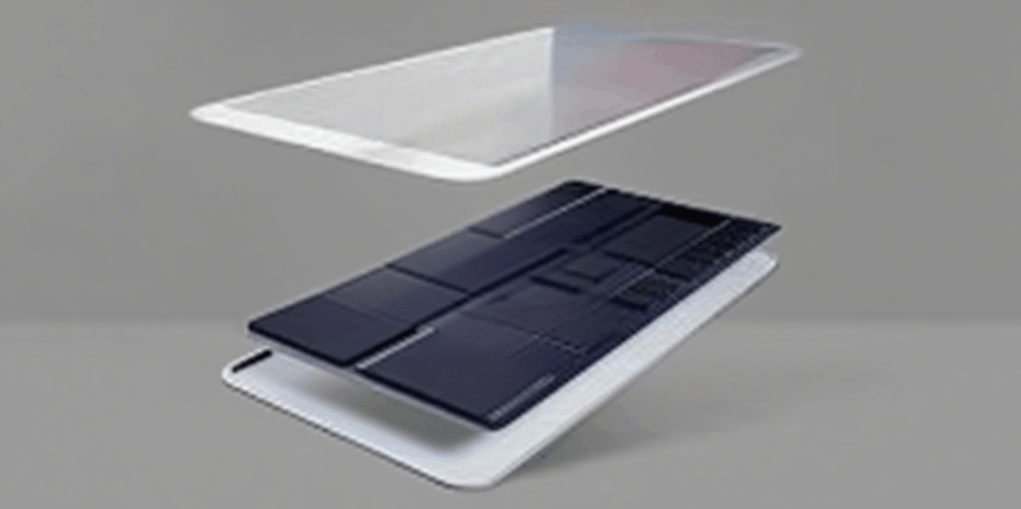

Classified by structure and application
1. Cover glass (front panel glass)
1.1 Function: Located on the front side of the photovoltaic module, it directly receives sunlight and must have high light transmittance, weather resistance (UV resistance, resistance to wind and rain erosion), mechanical strength (impact resistance), and anti-glare performance.
1.2 Specifications**: The thickness is typically 2.0 mm, 2.5 mm, or 3.2 mm (mainstream), with some ultra-thin products reaching 1.6 mm to reduce the weight of the module.
2. Backplate glass (rear panel glass)
2.1. Function: Located on the back of the photovoltaic module, it primarily serves insulation, moisture-proofing, and support functions. It has low requirements for light transmittance (even ordinary glass can be used), but must possess excellent corrosion resistance and insulation properties.
2.2 Application: Traditional modules typically use thin-film back panels (such as TPT, TPE), but glass back panels, which offer superior aging resistance (with a lifespan of over 25 years), are widely adopted in double-glass modules to enhance module reliability.
3. Double-glass module-specific glass
3.1 Features: Consists of two glass panels (front panel + back panel) with photovoltaic cells sandwiched between them, eliminating the need for a metal frame. This design results in lighter weight, superior wind and sand resistance, and enhanced weather resistance, while also enabling dual-sided power generation (the back panel captures reflected light).
3.2 Requirements: The front panel is made of ultra-clear rolled glass, while the back panel can be either ultra-clear glass or standard glass. Some products undergo tempering treatment to enhance strength.
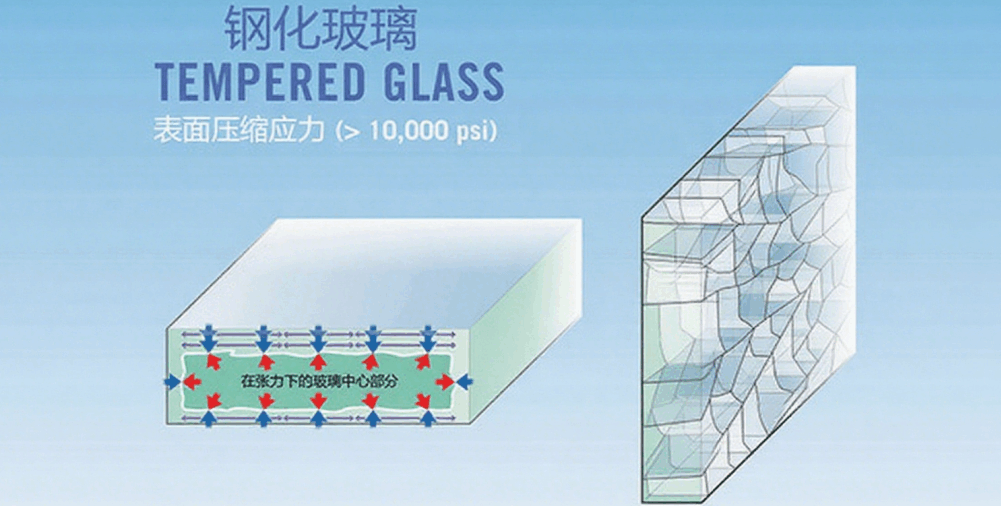
Classified by processing technology
1. Tempered photovoltaic glass: Through high-temperature tempering treatment, compressive stress is formed on the glass surface, resulting in impact resistance that is 3-5 times higher than ordinary glass. When broken, it shatters into blunt-edged particles, offering higher safety and making it the mainstream choice for photovoltaic modules.
2. Coated photovoltaic glass: A anti-reflective coating (such as SiO₂ or TiO₂) is applied to the glass surface to further reduce light reflectance (to below 5%) and enhance light transmittance. Some products also feature weather-resistant or anti-soiling coatings to enhance corrosion resistance and self-cleaning capabilities.
3. Ultra-thin photovoltaic glass has a thickness of less than 2.0 mm (e.g., 1.1 mm, 1.6 mm), produced via float or roll-forming processes, featuring lightweight and good flexibility. It is suitable for flexible photovoltaic modules, BIPV, and other applications with specific requirements for weight and form.

Special Types
1. Transparent Photovoltaic Glass (Semi-Transparent)** Used in BIPV photovoltaic curtain walls or skylights, this glass maintains a certain level of transparency while ensuring power generation by adjusting the spacing between solar cells or using transparent cell technology, thereby meeting building lighting requirements.
2. Anti-glare photovoltaic glass Features a special textured surface design or coating treatment to reduce glare from strong sunlight, making it suitable for photovoltaic power plants located near residential areas or major transportation routes. These categories of photovoltaic glass achieve performance optimization through different design approaches, addressing the diverse requirements of photovoltaic modules in terms of power generation efficiency, reliability, and application scenarios. Especially in the BIPV field, multifunctional photovoltaic glass is emerging as a key trend.
-
Photovoltaic glass
Aug 08, 2025
-
Best villa design solutions
Aug 08, 2025
-
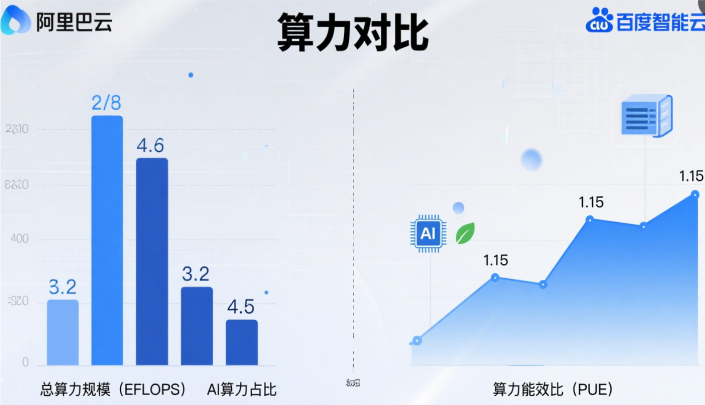
Aliyun VS Baidu Cloud
Jul 19, 2025
-
Smart factory network cabling
Jul 19, 2025
-
Full analysis of wiring test tools
Jul 19, 2025
-
Enterprise network cabling
Jul 19, 2025
-
Can you do smart control without the Internet
Jul 19, 2025
-
Principle of whole house intelligent control
Jul 18, 2025
-
Specifications and functions of light modules
Jul 18, 2025
-
Fiber optic engineering
Jul 18, 2025
-
Common classifications and their specific types:
Jul 18, 2025
-
Parking fee system
Jul 14, 2025
-
Video face recognition big data system
Jul 14, 2025
-
Starlink is a low-orbit satellite launched by SpaceX
Jul 14, 2025
-
5G base station project
Jul 14, 2025
-
5G and Starlink overview
Jul 14, 2025
-
Internet Data Center (IDC)
Jul 11, 2025
-
Enterprise LAN solutions
Jul 10, 2025
-
Video transmission theory
Jul 10, 2025
-
Patented technology and marked RJ45 crystal head
Jul 10, 2025
-
Advantages and disadvantages of intelligent control
Nov 30, 2024
-
Video Streaming Data Center
Nov 30, 2024
-
Computer Centre
Nov 30, 2024