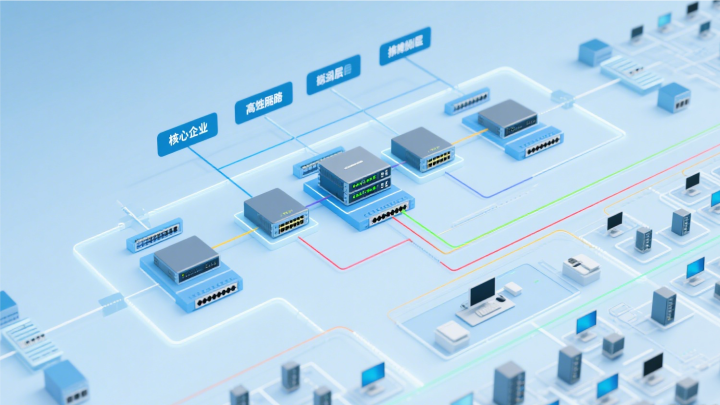
Enterprise LAN solutions
Overall Objective To build an efficient, safe, stable and enterprise business development LAN, to ensure the internal information transmission, resource sharing and normal operation of business systems, and to have good scalability to meet the future development needs of the enterprise.

Demand Analysis: Information Transmission: Ensure rapid and accurate information exchange between internal departments and terminals, including documents, data, emails, etc. Resource Sharing: Facilitate resource sharing of internal servers, printers, storage devices, etc., to enhance resource utilization efficiency. Business System Operations: Guarantee stable and efficient operation of enterprise business systems such as ERP and OA systems, preventing network bottlenecks and failures. Network Security: Prevent unauthorized access to networks and sensitive information leaks, block external network attacks, and protect corporate data security. Wireless Office: Meet employees' wireless office needs by providing stable and secure wireless network connectivity. Scalability: The network should be easily expandable to accommodate growing business scale and new terminal devices or service modules.

Network topology
The enterprise's local area network (LAN) adopts a star topology with the following configuration: The core switch (specific model A) supports high-speed data transmission at 1000Mbps, featuring redundant power supply and cooling systems to ensure stable operation. This setup meets current and future core data exchange requirements. Access switches in departments connect via Category 6 cables (6e), which provide higher transmission frequency and bandwidth to minimize signal interference and ensure reliable data transfer. Switch models vary by departmental terminal count: Departments with more terminals (e.g., Production and Sales) use model B (48 ports supporting Gigabit Ethernet), while departments with fewer terminals (e.g., Administration and Finance) opt for model C (24 ports with Gigabit Ethernet and better cost-effectiveness). All devices (computers, printers, etc.) connect directly to their respective departmental access switches. This centralized management structure allows quick troubleshooting when nodes fail without affecting others. Additionally, both core and access switches reserve ports for future expansion, enabling rapid network integration when adding new devices or departments.
Network equipment selection
Core Switch: Select model [specific model A]. Selection rationale: This switch features high bandwidth to support high-speed data transmission for enterprise networks, redundant power supply and cooling systems that enhance equipment reliability while minimizing network outages caused by power or fan failures, and supports multiple routing protocols with network management capabilities for centralized administration and configuration.

Access switch:
[Specific model B]: Suitable for departments with a large number of terminals. 48 ports can meet the access of a large number of devices. Gigabit Ethernet rate ensures the efficiency of data transmission, and supports VLAN division to facilitate network isolation and management between departments.
[Specific model C]: Suitable for departments with a small number of terminals. The 24 ports can meet the requirements, and it also has gigabit Ethernet rate and VLAN function, which is cost-effective.
Router: Select [specific model D]. This router supports multiple access methods (such as ADSL, fiber optic, etc.), can achieve the connection with external network, has strong routing forwarding capability and security functions, can filter and control the data in and out of the network, to ensure the security and stability of enterprise network and external network communication.
Firewall: Select [specific model E]. This firewall has the functions of state detection, intrusion prevention, VPN, etc., which can effectively block external network attacks such as virus, Trojan horse, hacker intrusion, etc., and control the access of internal network users to limit unauthorized users to access sensitive resources.
Wireless Access Points: Select the [Specific Model F] wireless access point based on the size and layout of your office space. This model supports the 802.11ac protocol, delivering high-speed wireless transmission with extensive coverage and multi-user connectivity. Deploy multiple access points evenly across the office to ensure comprehensive signal coverage and meet employees' wireless work requirements. Additionally, the access points feature WPA2-Enterprise encryption and 802.1X authentication for secure network protection.
IP address planning
Using the subnet division method, the enterprise LAN is divided into multiple subnets, each subnet corresponds to a department, easy to network management and troubleshooting.
The enterprise LAN employs an IP address segment of 192.168.0.0/24 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. Subnets are allocated based on terminal counts across departments: Administration Department (20 terminals): Subnet 192.168.0.0/27 with available IP addresses ranging from 192.168.0.1-192.168.0.30, gateway 192.168.0.31; Finance Department (15 terminals): Subnet 192.168.0.32/27 with available addresses from 192.168.0.33-192.168.0.62, gateway 192.168.0.63; Sales Department (50 terminals): Subnet 192.168.0.64/26 with available addresses from 192.168.0.65-192.168.0.126, gateway 192.168.0.127; Production Department (80 terminals): Subnet 192.168.0.128/25 with available addresses from 192.168.0.129-192.168.0.254, gateway 192.168.0.255. Server area: including ERP server, OA server, etc., the subnet address is 192.168.1.0/28, the available IP address range is 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.14, and the gateway is 192.168.1.15.
All terminal devices use static IP address allocation, which is assigned and recorded by the network administrator to avoid address conflicts.
Cyber security strategy
User authentication: The 802.1X authentication method is adopted. All users must input their username and password for authentication before accessing the network, and only authenticated users can access network resources. For sensitive devices such as servers, a more strict authentication method, such as USB Key authentication, is adopted.
Access Control: By using VLAN technology to partition departments into separate subnets, network isolation between departments is achieved. Additionally, access control lists (ACLs) are configured on core switches and firewalls to restrict access permissions between different subnets. For example, production departments are prohibited from accessing sensitive data in the finance department.

Data encryption: The sensitive data in the enterprise, such as financial data and customer information, is stored and transmitted by encryption technology to prevent data leakage.
Virus protection: Antivirus software is installed on all terminal devices and servers, and the virus database is updated regularly. Meanwhile, a virus protection wall is deployed on the gateway to scan the data packets in and out of the network for viruses and prevent virus intrusion.
Security system: Formulate strict network security system to regulate users' network behavior, such as prohibiting private IP address change, prohibiting access to illegal websites, and regularly changing passwords. Strengthen the network security awareness training of employees and improve their security prevention ability.
Cabling scheme
Cable selection: The indoor wiring uses category 6 unshielded twisted pair (UTP), which has high transmission performance and anti-interference ability, and can meet the transmission requirements of Gigabit Ethernet.

Cabling mode: Horizontal cabling: From the access switch of each department to the terminal equipment, it is carried out by ceiling or floor under dark laying to avoid cable exposure affecting appearance and safety.
Vertical cabling: From the core switch to the access switch on each floor, the weak current well in the bridge is laid to facilitate management and maintenance.
Information point layout: Arrange information points reasonably according to the number and location of terminal equipment in each department. At least one data information point and one voice information point should be set up for each office, and sufficient information points should be set up in the server room and equipment room according to the equipment requirements.
Outdoor cabling (if required) When an enterprise has multiple office buildings needing LAN connectivity, fiber optic cables are employed for outdoor installations. These cables offer advantages including long transmission distances, high bandwidth, and strong interference resistance. Outdoor fiber optic systems are installed through direct burial or overhead methods. For direct burial, they must be installed below permafrost layers with proper protective measures. For overhead installations, cables should be securely anchored to utility poles to prevent damage from wind and rain exposure.

Network management and maintenance
Network Management System: Deploy a network management system to monitor network devices, servers, and terminal equipment in real time, enabling timely detection and alerts for network failures. Through this system, administrators can view network topology, device status, traffic statistics, and other critical metrics, facilitating effective management and analysis.
Fault Troubleshooting Mechanism: Establish a comprehensive troubleshooting mechanism. When network failures occur, network administrators should follow the principle of "easier tasks first, local issues resolved before remote ones" when troubleshooting. First, check terminal devices and connection lines. If no issues are found, proceed to inspect access switches and core switches. Finally, examine firewalls and routers. Simultaneously, document fault symptoms, troubleshooting processes, and solutions to form a troubleshooting report, which will serve as a reference for future incident handling.
Regular Maintenance: Perform routine maintenance on network devices, including cleaning equipment, checking power supplies and fans, and updating firmware. Conduct periodic network cable tests to verify transmission performance and connection status, replacing aged or damaged cables promptly. Back up network configuration files and critical data regularly to prevent data loss.
-
fibre-optical
Jul 22, 2025
-
Classified by control technology
Jul 22, 2025
-
Aliyun VS Baidu Cloud
Jul 19, 2025
-
Smart factory network cabling
Jul 19, 2025
-
Full analysis of wiring test tools
Jul 19, 2025
-
Enterprise network cabling
Jul 19, 2025
-
Can you do smart control without the Internet
Jul 19, 2025
-
Principle of whole house intelligent control
Jul 18, 2025
-
Specifications and functions of light modules
Jul 18, 2025
-
Fiber optic engineering
Jul 18, 2025
-
Common classifications and their specific types:
Jul 18, 2025
-
Parking fee system
Jul 14, 2025
-
Video face recognition big data system
Jul 14, 2025
-
Starlink is a low-orbit satellite launched by SpaceX
Jul 14, 2025
-
5G base station project
Jul 14, 2025
-
5G and Starlink overview
Jul 14, 2025
-
Internet Data Center (IDC)
Jul 11, 2025
-
Enterprise LAN solutions
Jul 10, 2025
-
Video transmission theory
Jul 10, 2025
-
Patented technology and marked RJ45 crystal head
Jul 10, 2025
-
Advantages and disadvantages of intelligent control
Nov 30, 2024
-
Video Streaming Data Center
Nov 30, 2024
-
Computer Centre
Nov 30, 2024