Common classifications and their specific types:

1.**Classification by Structure** - **Stranded Optical Cable**: Multiple optical fibers are tightly twisted around a central core, offering compact construction with excellent mechanical properties. This design accommodates various fiber counts and is suitable for diverse installation environments. - **Centralized Bundled Tube (CUT) Optical Cable**: Fibers are housed within a central tube filled with grease to prevent water ingress and provide shock absorption. Featuring low profile and lightweight construction, it ensures easy installation. - **Rigged Optical Cable**: Fibers are placed in grooves within a rigid frame (typically plastic or metal), which effectively protects the fibers while enhancing mechanical strength and stability. This type is ideal for long-distance communication systems and outdoor environments with harsh conditions. - **Stranded Tape Optical Cable**: Multiple fibers are arranged in tape form and combined into cables. This high-density integration significantly boosts transmission capacity, making it ideal for applications requiring large-capacity data transfer.

2.**Classification by Installation Method** - **Aerial Optical Cable**: Installed overhead using steel strands or self-supporting structures to suspend cables. Suitable for constructing communication lines across rivers, valleys, and urban streets with complex terrain. - **Pipeline Optical Cable**: Installed in underground pipelines, protected from external mechanical damage and corrosion. Ideal for urban communication network construction. - **Direct Burial Optical Cable**: Embedded directly underground, requiring excellent waterproof, moisture-proof, and anti-corrosion properties. Commonly used for long-distance communications and rural area line installations. - **Submarine Optical Cable**: Designed for communication lines spanning rivers, lakes, and oceans. Requires high strength, superior waterproofing, and corrosion resistance.

3.**Classification by Plastic Sheathing Method** - **Tight-Placed Optical Cable**: The fiber is tightly enclosed within a plastic sheath without gaps, offering excellent mechanical strength and interference resistance. Ideal for indoor and short-distance communications. - **Loose-Placed Optical Cable**: The fiber is placed in a loose sheath with gaps between the fiber and sheath, allowing oil-based fillers to cushion external forces and provide waterproofing. Suitable for outdoor and long-distance applications. - **Stranded Tube Optical Cable**: Multiple fibers are bundled into a tube before being sheathed. This simple structure reduces costs, making it ideal for user access networks and short-distance communication. - **Striped Multi-Core Unit Optical Cable**: Composed of multiple fiber strips containing individual fibers, this design enables high-capacity, high-density transmission. Commonly used in backbone communication networks and data centers requiring large-scale fiber transmission.
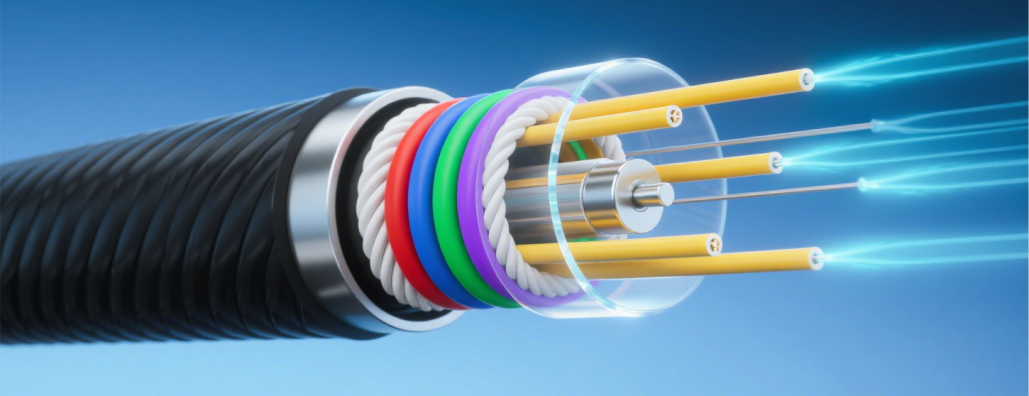
4.**Classification by Application Environment** - **Outdoor Optical Cables**: Designed for outdoor installations including overhead, direct burial, and conduit methods, featuring excellent waterproofing, moisture resistance, UV protection, and corrosion resistance. - **Indoor Optical Cables**: Installed in building environments such as offices and server rooms, requiring flame-retardant properties and flexibility for easy installation. - **Specialized Optical Cables**: Including submarine cables, all-dielectric self-supporting cables (ADSS), fiber composite overhead ground wire cables (OPGW), coiled cables, and rodent-resistant cables, tailored for specific environments and application scenarios.
5.**Classification by Network Layer** - **Long-haul Optical Cable**: Designed for long-distance communication between cities and regions, these cables typically feature high transmission capacity and extended reach, serving as the backbone of communication networks. - **City telephone optical cable**: Primarily used in urban communication infrastructure development, connecting telephone exchanges, base stations, and other telecom facilities within city areas. - **Access optical cable**: Used to connect user terminal devices to network access points, such as fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) and fiber-to-the-building (FTTB) applications.
6.**Classification by Reinforcement Component Configuration** - **Center Reinforcement Cables**: Reinforcement components are positioned at the center of optical cables, such as stranded cables and skeleton cables, which effectively enhance tensile strength. - **Distributed Reinforcement Cables**: Reinforcement components are distributed across various sections of the cable, like side-strengthened cables on bundled conduits or flat cables, improving lateral compression resistance and flexibility. - **Sheath Reinforcement Cables**: Reinforcement components are embedded in the cable's sheath, such as steel wire-encased bundled conduits and PE composite outer-sheathed cables with fine steel wires, enhancing mechanical durability and corrosion resistance. - **Steel Tube Micro-Cables**: Utilizing steel tubes as both reinforcement and protective structures, these cables demonstrate high strength and interference resistance, making them suitable for specialized environments and applications.
7.**Classification by Fiber Type** - **Multimode Fiber Optic Cable**: Utilizes multimode fibers to transmit multiple optical signal modes, ideal for short-distance, high-bandwidth applications such as LANs and data center interconnections. - **Single-mode Fiber Optic Cable**: Uses single-mode fibers to transmit only one optical signal mode, suitable for long-distance, high-speed communication applications including long-distance communications and backbone network construction. - **Single-core Optical Cable**: Contains only one fiber core, ideal for scenarios requiring fewer cores, such as fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) cables and indoor patch cords. - **Multi-core Optical Cable**: Includes two or more fiber cores, available in configurations like dual-core, quad-core, six-core, eight-core, and twelve-core variants to meet diverse communication needs and application requirements.
8.**Classification by Protective Layer Material** - **Standard Optical Cable**: The protective layer is typically made of polyethylene (PE) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offering excellent flexibility and weather resistance. It is suitable for communication line construction in general environments. - **Flame-Resistant Optical Cable**: The protective layer uses flame-retardant plastics such as flame-retardant polyethylene (FRPE) or flame-retardant polyvinyl chloride (FRPVC), effectively preventing fire spread. This type is ideal for high fire safety requirements. - **Nylon-Resistant Ant-Rat Optical Cable**: The protective layer incorporates materials like nylon with ant and rodent-resistant properties, preventing damage from termites and rodents. It is ideal for areas with frequent termite and rodent activity.
-
fibre-optical
Jul 22, 2025
-
Classified by control technology
Jul 22, 2025
-
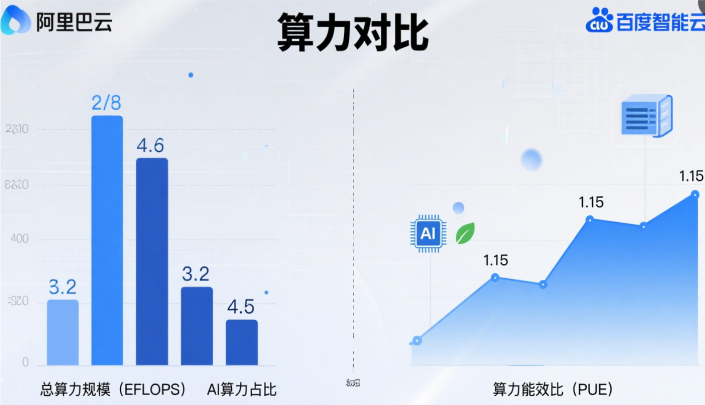
Aliyun VS Baidu Cloud
Jul 19, 2025
-
Smart factory network cabling
Jul 19, 2025
-
Full analysis of wiring test tools
Jul 19, 2025
-
Enterprise network cabling
Jul 19, 2025
-
Can you do smart control without the Internet
Jul 19, 2025
-
Principle of whole house intelligent control
Jul 18, 2025
-
Specifications and functions of light modules
Jul 18, 2025
-
Fiber optic engineering
Jul 18, 2025
-
Common classifications and their specific types:
Jul 18, 2025
-
Parking fee system
Jul 14, 2025
-
Video face recognition big data system
Jul 14, 2025
-
Starlink is a low-orbit satellite launched by SpaceX
Jul 14, 2025
-
5G base station project
Jul 14, 2025
-
5G and Starlink overview
Jul 14, 2025
-
Internet Data Center (IDC)
Jul 11, 2025
-
Enterprise LAN solutions
Jul 10, 2025
-
Video transmission theory
Jul 10, 2025
-
Patented technology and marked RJ45 crystal head
Jul 10, 2025
-
Advantages and disadvantages of intelligent control
Nov 30, 2024
-
Video Streaming Data Center
Nov 30, 2024
-
Computer Centre
Nov 30, 2024