- Language
Customizable R&D
The process of customizing products is a systematic engineering that starts from user needs, goes through layers of polishing, and finally achieves large-scale production. Each link carries the responsibility of precise docking and quality control. Our specific process is as follows:

1、 Pain point requirement mining and analysis
This is the starting point for customized products, which requires deep penetration into users' usage scenarios and industry pain points. Conduct in-depth decoding of requirements through multidimensional research, such as conducting one-on-one user interviews to capture their inconvenience and complaints when using existing products; Conduct industry trend analysis and predict potential unmet market demands; Organize internal brainstorming to identify valuable demand points based on one's own technological advantages. Afterwards, a list of requirements will be compiled to clarify the core issues that the product must address, the expected functional indicators, and the implicit demands of users regarding appearance, materials, cost, and other aspects, laying a solid foundation for subsequent processes.
2、 Design scheme formulation and optimization
Based on the identified pain points and requirements, the design team embarks on a journey of creative transformation. First, draw a preliminary conceptual design diagram based on the requirements list, covering core elements such as product structure layout, functional modules, appearance, etc., to make abstract requirements concrete. Subsequently, a digital model was constructed through 3D modeling to simulate the assembly relationship and operational status of the product, and to identify design vulnerabilities. At the same time, interdisciplinary reviews are conducted in collaboration with engineering, production, and other departments to optimize the plan from the perspectives of technical feasibility, production process adaptability, and cost control. After multiple rounds of modifications, the final design plan is determined and detailed design drawings and BOM lists (material lists) are generated.
3、 Sample testing and iteration
Produce physical samples according to the design plan, and the samples should be as faithful as possible to the material, structure, and function of the final product. The testing phase adopts a dual track mode of "laboratory testing+scenario based trial": in the laboratory, the performance indicators (such as strength, durability, accuracy, etc.) and safety (such as electrical safety, environmental protection, etc.) of the samples are strictly tested through professional equipment; Scenario based trials invite target users to experience the sample in a real usage environment, collecting feedback on the sample's feel, ease of operation, functional satisfaction, and other aspects. Based on the test results, generate a problem report and adjust the design details accordingly. Repeat sample production and testing until all indicators of the sample meet the core needs of the user.
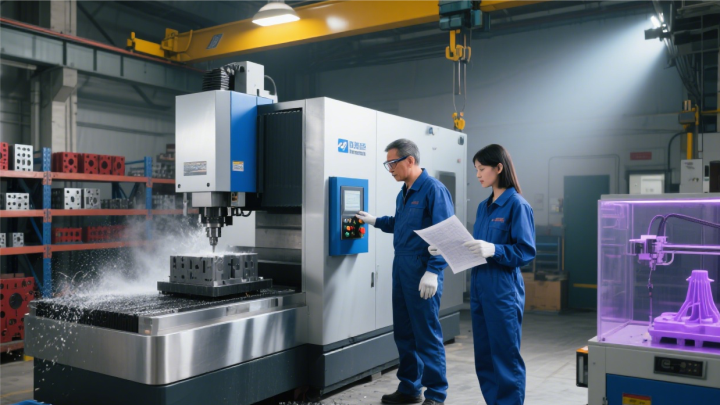
4、 Mold development and validation
After sample confirmation, it enters the mold development stage, which is a crucial step in achieving mass production of the product. Based on the structural complexity and material characteristics of the product, select appropriate mold materials (such as steel) and processing techniques (such as CNC machining, electrical discharge machining, etc.), and have a professional mold factory design and manufacture the mold. After the mold is completed, a trial mold is carried out to produce a small number of trial mold parts through injection molding, stamping and other processes, and to check whether their dimensional accuracy, surface quality, and fit with other components meet the design requirements. Correct the mold defects (such as burrs, shrinkage marks, etc.) that appear during the trial mold until the mold is stable and meets the standards, providing a qualified "tool mother machine" for subsequent production.

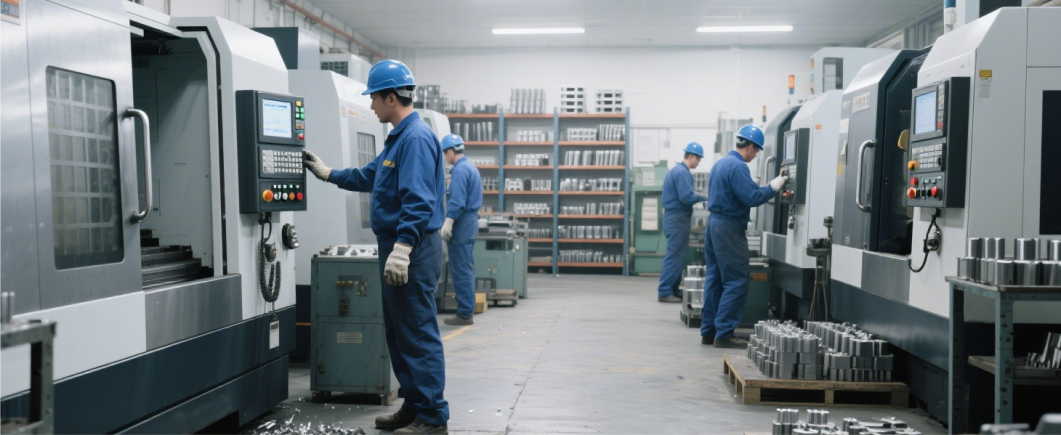
5、 Small batch production testing
Small batch production is a transitional link between sample and mass production, typically producing hundreds to thousands of products. At this stage, the focus is on verifying the stability of the production process, including whether the equipment debugging, process parameter setting, and personnel operation specifications of the production line are suitable for the product; Simultaneously verify the collaborative ability of the supply chain to ensure timely supply of raw materials and precise assembly of components. Conduct full inspection on small batch products, calculate the pass rate, analyze the causes of defective products, further optimize production processes and quality control procedures, form standardized production guidance documents, and accumulate practical experience for mass production.
6、 Mass production and delivery
After small-scale testing and verification, large-scale production has officially begun. According to the established production plan, coordinate the efficient operation of various links such as raw material procurement, component processing, final assembly, and quality inspection, and control production costs and cycles through automated production lines and refined management. Each batch of products must undergo strict sampling and full inspection to ensure compliance with quality standards. Ultimately, qualified products will be packaged and delivered according to the order requirements, while establishing an after-sales tracking mechanism to collect user feedback and provide data support for subsequent product iterations.
The entire customized product process is interconnected, from precise capture of requirements to continuous improvement in production, with customer satisfaction as the core goal at every step, ultimately achieving a complete closed-loop from creative conception to delivery.