- Language
Principle of whole house intelligent control
The essence of whole-home intelligent control lies in its closed-loop logic of "Perception-Connection-Prediction-Execution", which coordinates various home devices, environmental conditions, and user needs to enable automated management or remote operation. This principle can be broken down into four core components: "Hardware foundation + communication link + control hub + interaction logic". These elements work together to complete the entire process from instruction input to device response.

1. Hardware foundation: the terminal carrier of perception and execution
The foundation of smart home systems lies in the integration of sensing and actuating devices. Sensing devices function as "nerve endings," collecting environmental data and user activities. For instance, temperature/humidity sensors monitor indoor conditions in real time, motion detectors detect human presence, while door/window sensors track opening/closing status. These devices convert physical signals (temperature, light, infrared) into digital signals through built-in chips, providing actionable intelligence for subsequent controls. Actuating devices serve as "muscle units," receiving commands to perform specific operations. Examples include smart lighting that adjusts brightness and color temperature, climate-controlled air conditioners switching modes, and smart curtains managing opening/closing ratios. Typically equipped with intelligent modules (e.g., WiFi modules or Bluetooth chips), these devices can process external commands and execute corresponding actions.
2. Communication link: the "information superhighway" for device interconnection
The signals collected by the sensing equipment and the instructions issued by the control center need to be transmitted between the equipment through communication protocols. The current mainstream communication technologies have their own applicable scenarios:
WiFi: Suitable for devices that need to directly connect to the Internet (such as smart speakers, cameras), fast transmission speed but high power consumption, suitable for devices that do not need long standby;
Zigbee/Z-Wave: Low power consumption, strong anti-interference, suitable for small data devices such as sensors and switches. It can aggregate signals through the "gateway" and connect to the network, supporting multi-device networking;
Bluetooth (BLE): suitable for short distance device linkage (such as mobile phone and smart door lock close range unlock), low power consumption and low cost;
KNX: Industrial bus protocol, which is extremely stable and often used in lighting and air conditioning systems for large residential or commercial Spaces, and supports complex scenario linkage.
These protocols are like different types of "languages", and the gateway is the "translator" —— When devices use different protocols (such as Zigbee sensor and WiFi air conditioner), the gateway can achieve signal conversion to ensure information transmission across protocols.
3. Control center: the "brain" of intelligent decision-making
The control center is the core of the system, responsible for receiving data, parsing requirements and issuing instructions, which is equivalent to the role of "brain". Its core functions have two:
Data processing: summarize the environmental data (such as "temperature 28℃+ people activity") from the sensing equipment, and generate execution logic by combining preset rules (such as "temperature>26℃ automatic air conditioning") or user instructions (such as voice "turn on the living room light");
Instruction Distribution: The processed logic is converted into device-readable commands (e.g., sending "Cooling Mode + 24℃" signals to air conditioners) and transmitted via communication links to corresponding execution devices. Common control hub formats include smart speakers (such as Xiao Ai Classmate and Tmall Genie, which combine voice interaction with control functions), professional gateways (like Apple HomeKit Gateway and Xiaomi Multimode Gateway), and central control screens (integrating touch interfaces and scenario controls). Some high-end systems also incorporate AI algorithms that optimize decisions through learning user habits (e.g., automatically adjusting curtain opening/closing times based on daily routines).
4. Interaction logic: the "input channel" of user needs
The control instructions of the whole house intelligence can be triggered in a variety of ways to form flexible interaction logic:
Automated trigger: triggered by environmental changes or time without user operation. For example, when the light sensor detects sunset (light <300lux) + doors and Windows are closed, the main living room lamp is automatically turned on;
Scenario-based linkage: Users preset "scenario mode" to activate multi-device collaboration with one click. For example, "home mode" triggers a combination of actions such as "unlock the door lock → turn on the entrance light → adjust the air conditioner to 25℃ → open the curtains";
Active control: Direct commands can be issued through voice commands ("Xiao Ai, turn off the bedroom lights"), mobile apps (to remotely view camera feeds), or touch controls (by pressing smart switches). The core of these interaction methods lies in converting user needs or environmental changes into standardized instructions, which are then distributed by the central control hub to corresponding devices for execution.
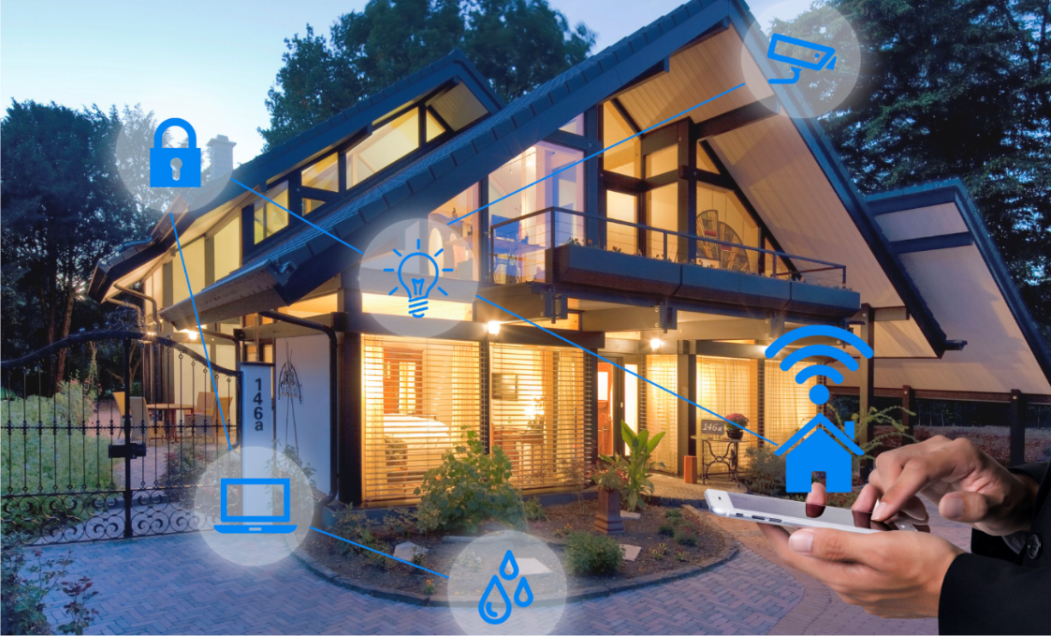

5. Core logic: A closed loop from "instruction input" to "device response"
Take "turning on the air conditioner automatically when you go home in summer" as an example, the complete process can be broken down into:
Perception: The door and window magnetic sensor detects "the door is open" (someone enters), and the temperature and humidity sensor sends back "the indoor temperature is 30℃";
Transmission: The two sensors send signals to the gateway through Zigbee protocol, and the gateway forwards the data to the control center (such as smart speaker);
Decision: The control center matches the preset rules. "Someone enters and the temperature is>26℃ → turn on the air conditioner for refrigeration" to generate instructions;
Operation: The command is transmitted via WiFi to the smart air conditioner, which then switches to cooling mode and sets the temperature at 24℃. The entire process flows seamlessly from "environmental sensing" to "device execution", with real-time status monitoring through the mobile app or manual intervention, achieving a balance between "smart automation" and "human control".
6.Conclusion: The essence of whole-house intelligence is "data-driven collaborative control"
In essence, the core of whole-house intelligent control lies in three key processes: information acquisition through sensors, data transmission via communication protocols, and execution of commands by the central controller. This system ultimately achieves "on-demand regulation". Whether it's a simple "lighting upon arrival" or sophisticated features like "automatic power-off, window closure, and security activation when leaving home", all these functions essentially extend this fundamental logic——. By leveraging technological solutions to reduce manual intervention, devices autonomously coordinate based on environmental conditions and user needs.
-
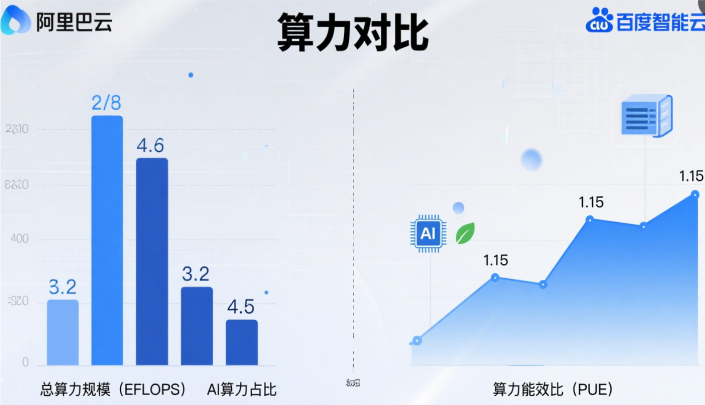
Aliyun VS Baidu Cloud
Jul 19, 20254760
-
The Importance of Network Cabling for Smart Factories
Jul 19, 20254742
-
Full analysis of wiring test tools
Jul 19, 20254737
-
Enterprise network cabling
Jul 19, 20252432
-
Can you do smart control without the Internet
Jul 19, 20253496
-
Principle of whole house intelligent control
Jul 18, 20253510
-
Specifications and functions of light modules
Jul 18, 20254631
-
Fiber optic engineering
Jul 18, 20252436
-
Common classifications and their specific types:
Jul 18, 2025186
-
Parking fee system
Jul 14, 2025338
-
Video face recognition big data system
Jul 14, 20253414
-
Starlink is a low-orbit satellite launched by SpaceX
Jul 14, 20254631
-
5G base station project
Jul 14, 20253727
-
5G and Starlink overview
Jul 14, 20254750
-
Enterprise LAN security access control system project
Jul 14, 20253517
-
Internet data centers are the nerve center of the digital economy
Jul 14, 20252431
-
Internet Data Center (IDC)
Jul 11, 20254609
-
Enterprise LAN solutions
Jul 10, 20253342
-
Video transmission theory
Jul 10, 20258892
-
Patented technology and marked RJ45 crystal head
Jul 10, 202533733
-
The relationship between network and intelligent control
Nov 30, 20245264
-
Advantages and disadvantages of intelligent control
Nov 30, 20244606
-
Video Streaming Data Center
Nov 30, 20244653
-
Computer Centre
Nov 30, 20243378